What is a Politically-Exposed Person (PEP)?
PEPs, or politically exposed persons, are individuals with significant political influence or those who have close associations with high-ranking government officials. Due to their position and relationships, PEPs may have an increased risk of being involved in activities that make them vulnerable to financial crime.
What is a Politically-Exposed Person (PEP)?
PEPs, or politically exposed persons, are individuals with significant political influence or those who have close associations with high-ranking government officials. Due to their position and relationships, PEPs may have an increased risk of being involved in activities that make them vulnerable to financial crime.
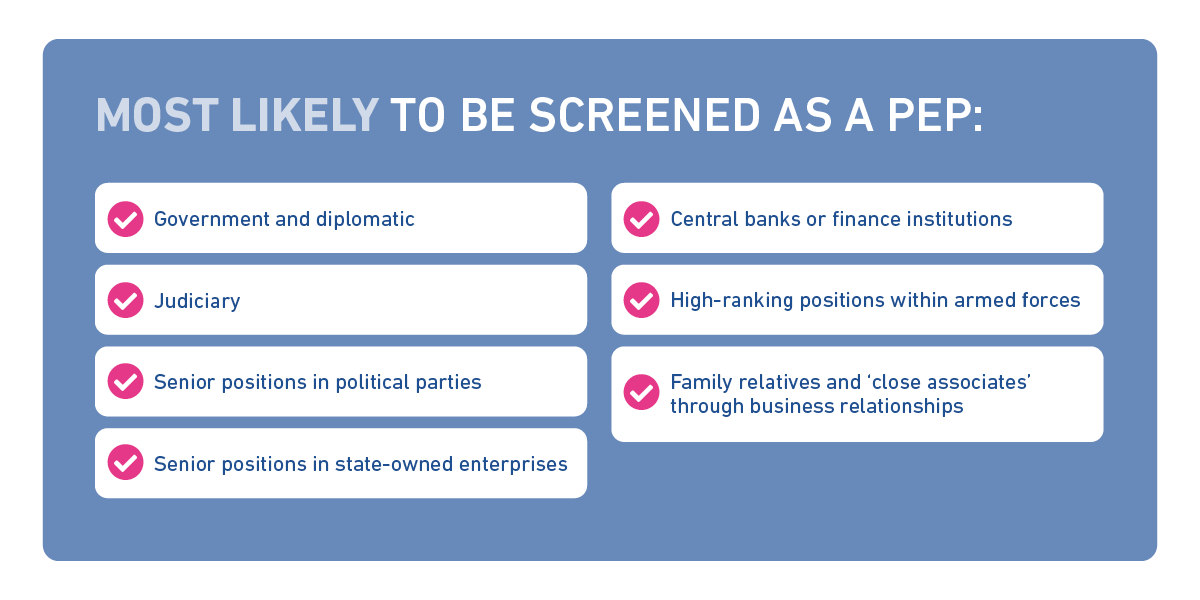
Typically, people working in the following positions or bodies are most likely to be screened as a PEP:
- Government and diplomatic
- Judiciary
- Senior positions in political parties
- Senior positions in state-owned enterprises
- Central banks or finance institutions
- High-ranking positions within armed forces
- Family relatives and ‘close associates’ through business relationships
What is a PEP check?
PEP checks aim to protect financial institutes from becoming involved with illicit financial activities. Robust PEP checks identify and conduct customer due diligence checks on any politically exposed person to reduce the risk of bribery and corruption.
During PEP checks and screening, organisations can verify whether a customer or client is a PEP. This is achieved by checking databases and PEP lists provided by government agencies. By identifying PEPs, companies can manage the potential associated risks.
These checks are crucial for financial institutions, regulatory bodies, and businesses to carry out. They are an important part of anti-money laundering and know your customer efforts.
What are financial sanctions?
Financial sanctions are restrictive measures imposed on individuals by governments or regulatory bodies. These sanctions are placed to achieve a specific policy objective and prohibit a firm from carrying out transactions with an individual or business.
Restrictive financial sanction measures include freezing of financial assets, restrictions on travel, and trade restrictions.
States, non-state entities, and individuals that pose a threat to international security can be subject to financial sanctions.
What is sanction screening?
Sanction screening is a process by which financial institutes, business and organisations identify whether individuals they deal with are subject to sanctions or restrictions imposed by government bodies. This helps ensure compliance, prevent involvement with illicit financial activities, and manage reputational risk.
Key aspects of sanction screening include watchlists and sanctions lists provided by government agencies, automated screening tools to check customer databases efficiently and accurately, and real-time monitoring of transactions against sanction lists.
Who compiles the financial sanctions lists?
Financial sanction lists are compiled and published by government agencies and sanctioning bodies such as sovereign states, regional unions, and international organisations.
In the UK, HM Treasury’s Office for Financial Sanctions Implementation (OFSI) publishes and updates the list of those who are subject to financial sanctions imposed by the UK Sanctions and Anti-Money Laundering Act[1].
What is an AML sanction screening?
AML sanction screening is the process of identifying whether individuals are subject to financial sanctions due to involvement in money laundering or terrorism financing. The aim of AML sanction screening is to detect and prevent illicit interactions with individuals who pose a risk of financial crime.
What is AML sanction screening?
AML sanction screening is the process of identifying whether individuals are subject to financial sanctions due to involvement in money laundering or terrorism financing. The aim of AML sanction screening is to detect and prevent illicit interactions with individuals who pose a risk of financial crime.
Anti-money laundering checks are an important part of AML compliance. It is a legal requirement for companies to carry out these checks on customers and clients.
What is adverse media screening?
Adverse media screening is the review of a customer or prospect against negative news and information to assess potential risk from that individual.
This process allows financial and compliance organisations to assess negative or adverse information about an individual to calculate the risk of involvement in financial crimes and fraud.
Why are PEP and sanction screenings necessary?
PEPs and sanction screenings are necessary for businesses to mitigate and prevent risks associated with financial transactions. These activities and efforts prevent crimes such as bribery and corruption to secure business reputation, revenue, and capital.
Are PEPs and sanction screenings mandatory?
Politically exposed person checks and sanctions screenings are essential practices for financial institutes, regulatory bodies, and businesses. They are an integral part of the regulatory compliance framework and organisations must conduct these checks as part of the due diligence process.
The risk of inaccurate sanction checks
Sanction checks are mandatory for compliance but have the potential for inaccuracies in the screening process.
Inaccurate sanction checks can result in false positives and false negatives that can undermine the purpose of sanction screening and PEP checks.
Outdated sanction lists, name variations, and data quality issues can also lead to inaccurate matches or failures to identify an individual’s true identity.
The risk of inaccurate sanction checks is that individuals subject to sanctions can slip through the net and put financial institutes at risk of engaging in prohibited financial activities.
What is the process for PEP and sanction screening?
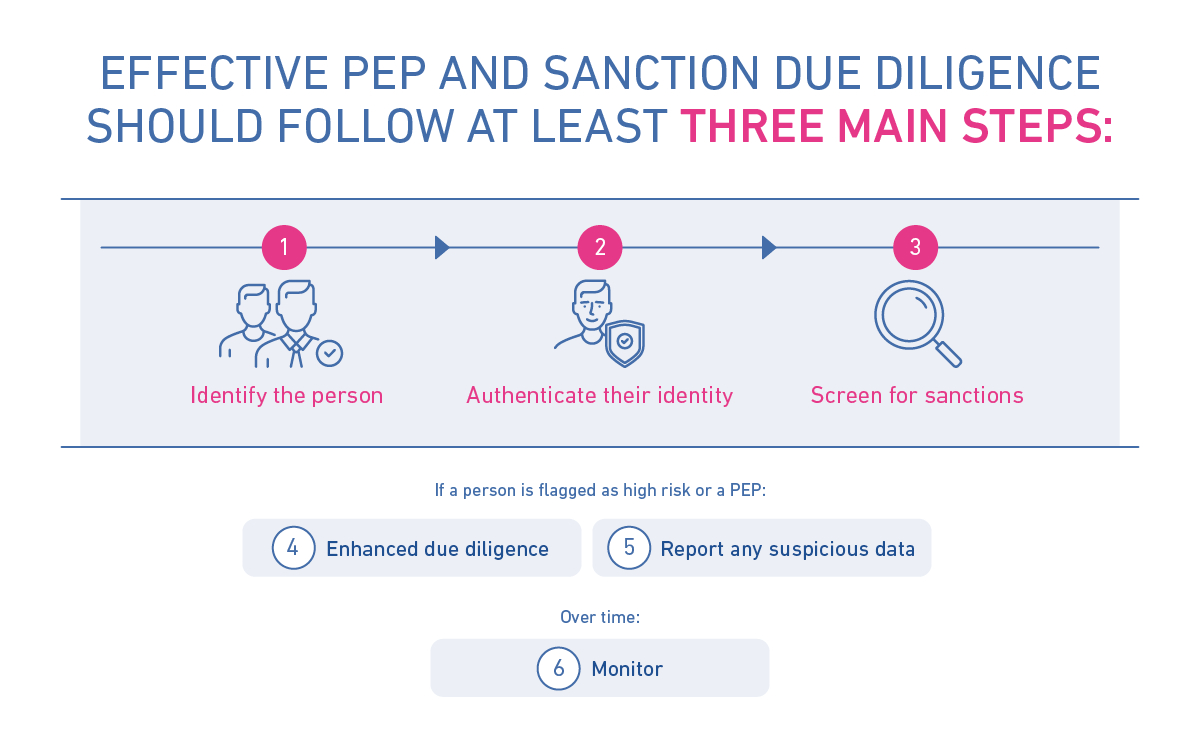
Effective PEP and sanction due diligence should follow at least three main steps:
- Identify the person: Collect data or documentation that identifies the person or decision-maker in question and their positions as Ultimate Beneficial Owners (UBOs) or Person of Significant Control (PSC) within organisations.
- Authenticate their identity: Validate that the person is who they claim to be through ID verification and by following Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols.
- Screen for sanctions: Review against sanctions lists and apply risk scoring to avoid dealing with sanctioned or risk-posing individuals.
Typically if a person is flagged as high-risk or is identified as a PEP, further actions need to be taken:
- Enhanced due diligence: Additional measures and procedures to check for potential financial crime or high-risk activities.
- Report any suspicious data: Activity by PEPs under sanctions or any suspicions about an individual should be reported with a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR).
Ultimately, individuals on the list may not initially present a risk, but could become a concern over time. That’s why continuous monitoring is crucial.
- Monitor: Screening lists are changing all the time, so monitoring will highlight and provide alerts about any changes to risk or new suspicious activity.
How can firms ensure compliance with PEPs and sanction screening requirements?
To comply with KYC and AML requirements, businesses must conduct PEPs and sanction checks as part of due diligence efforts.
For financial institutes and businesses, it is important to regularly update screening databases, establish robust compliance procedures, and integrate screening into the onboarding process to maintain ongoing compliance.
PEP and sanction screening solutions from Experian
At Experian, we offer PEP and sanction screening tools and solutions. Our three-step solution streamlines criminal screening and financial sanctions processes to improve the customer experience.
Using our tools, businesses can quickly identify, authenticate, and screen individuals to achieve greater due diligence.
For more information, speak to an expert today.
[1] The UK Sanctions List, GOV.UK








