Unravelling the power of digital decisioning
Shaping the future of data-driven decisions
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are inundated with an unprecedented amount of data and information. Making informed decisions with the data quickly and effectively has become a crucial factor for success. Enter digital decisioning—a transformative approach that harnesses the power of data, analytics, and automation to drive reliable and expedited decision-making.
This article delves into the world of digital decisioning, exploring its significance, components, and benefits.
The essence of digital decisioning
At its core, digital decisioning is the process of leveraging software solutions that use digital decisioning platforms or custom-built engines to author decision logic; use decision intelligence technologies such as machine learning and AI; use digital decisions in vertical and horizontal use cases; and manage the full decision logic lifecycle, including feedback loops, to continuously improve decision logic. It enables organizations to make well-informed choices by automating and optimising complex decision processes. By amalgamating data from various sources in real-time, including credit data, user behaviour, market trends, historical data, and external factors, digital decisioning ensures that timely decisions are not only data-driven but also contextually relevant.
Components of digital decisioning
- Continuous data feed: This is the lifeblood of digital decisions. Organisations normalise data from disparate sources to form comprehensive and accurate datasets. Customer data might include income, credit history, transactional data, bill payment, or digital footprint data; however, regardless of the sources, it’s critical that data is coalesced into a single, virtualised view.
- Advanced analytics and machine learning: Analytics and machine learning algorithms are deployed to extract meaningful insights from the collected data. These insights are used to model decision scenarios, predict outcomes, and uncover hidden patterns.
- Decision models: Decision models are created based on the insights derived from data analysis. These models define the rules and logic for making decisions, incorporating factors such as risk tolerance, business goals, and regulatory compliance.
- Direct feedback loop: Every decision has an outcome. For example, an automated loan offer is either accepted or declined by the customer. These outcomes — good and bad — automatically feed into the decisioning model, which enables the machine learning technology to “learn” which decisions are optimal, given the circumstances and customer profile. This enables the model to adapt and grow more accurately and precisely over time.
- Automation: Automation engines execute the decision models in real time, allowing for rapid and consistent decision-making without human intervention. This enhances efficiency and minimises the risk of errors. According to a 2022 Gartner poll, the CIO Agenda, more than 80% of companies plan to keep or grow their investment in automation solutions.
Use case
Respond faster to credit card applications and personalise cross-sell offers
Customers apply online for a credit card from a bank. As they’re being pre-qualified, digital decisioning will instantly analyse the customers’ accounts with the bank including disclosed and undisclosed cash flow. A digital decisioning software solution enables the bank to assess risk exposure and anticipate the customer’s immediate need(s), thereby automating the application assessment and approval steps to reduce approval times from weeks to minutes. Based on the bank’s comprehensive understanding of that customer at that moment, it triggers a personalised cross-sell offer for another relevant financial product, automatically boosting incremental revenue.
Continuous improvement loop: Advanced machine learning models improve decisioning quality
Conclusion
Digital decisioning marks a pivotal advancement in how choices are made in business. By harnessing the power of data, analytics, and automation, organisations can make faster, more accurate decisions that are aligned with their goals and market realities. As this technology continues to evolve, it will reshape industries and empower individuals to navigate the complex digital landscape with confidence.
Our decisioning management platform allows clients to operationalise the power of rich data, advanced analytics, and automated decisioning software to support the customer lifecycle. Its key differentiators include credit risk, fraud risk, and strategy expertise, fast deployment of strategies into test and production, empowerment of business users, and proactive monitoring of strategy performance by users. Its key use cases include reducing acquisition costs, credit risk, and fraud risk, and improving acceptance rate and the customer journey.
We have been named a Technology Leader in the August 2023 SPARK Matrix on Digital Decisioning Platforms report published by Quadrant Knowledge Solutions. The report highlights the growth of decisioning platforms and the changing market trends that are driving adoption, including the role machine learning and AI are playing in the technology market. This placement is proof that Experian offers best-in-class capabilities through market-leading data, orchestration and automation, advanced analytical models, decision performance, and reporting. Our cloud-based infrastructure enables a scalable and modular platform that allows our solutions to be suitable for customers of all sizes.
How can we help?
Our latest edition decision management platform, part of the PowerCurve platform, helps you to make better customer decisions even when operating in a dynamic business environment.
PowerCurve allows you to operationalise rich data and advanced analytics. It’s a unified, component-based platform for strategy design and execution, enriched with capabilities for credit risk decisioning, including marketing, identity and fraud, and affordability.
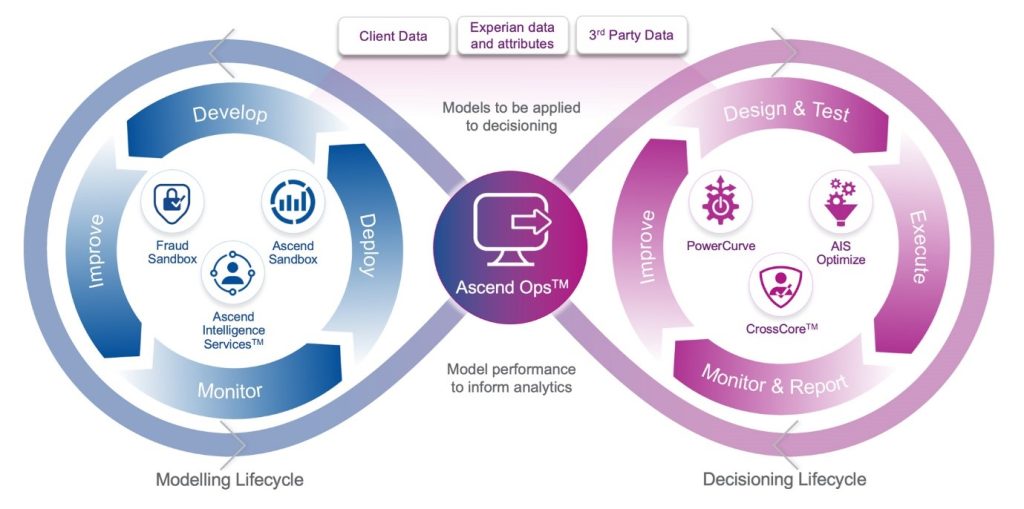
The infographic combines two loops, overarched with three types of data: Client data, Experian data and attributes, and third party data.
The first loop contains the modelling lifecycle, consisting of:
- Develop
- Improve
- Monitor
- Deploy
The associated products are Fraud Sandbox, Ascend Sandbox and Ascend Intelligence Services™.
The second loop contains the decisioning lifecycle, consisting of:
- Design and test
- Execute
- Monitor and report
- Improve
The associated products are PowerCurve, Ascend Intelligence Services™ and CrossCore.
These models are to be applied to decisioning and to inform analytics.









